An ERP Accounting Software is one that automates the tasks performed by various users in the finance department of a company. These users could be accounts clerks, accountants, or managers. The software could either be installed on Cloud Servers in which case it is called Cloud ERP or ERP on Cloud.
An accounting in ERP allows you to configure the system accurately so that all the transactions are accounted for accurately and reported automatically.
ERP Accounting Software is mostly used by the Finance department. The department has three major tasks, Corporate Finance and treasury (CF&T), Accounting and Reporting, and Financial Control.

Corporate Finance handles negotiations for raising long and short-term loans and restructuring of existing loans. They negotiate with investment managers for creating and marketing debt instruments like debentures that they sell to the investing community to raise capital. They are also responsible for handling investor relations and statutory compliance and reporting.
Treasury management is the task of planning, organizing and controlling the funds flow to ensure adequate liquidity for the company. The treasury department deals with investment of surplus cash and meeting working capital requirements. It also manages the relations with banks. CF&T is a separate team in the finance department.
Accounting and Reporting are the operational tasks of the finance department. These involve accounting for transactions, summarizing them, completing period end activities, posting to General Ledger, extracting key performance reports, and sharing them with the internal and external stakeholders.
Cost accounting involves tasks like setting up of cost standards, tracking cost elements, analyzing variances, and reporting the cost information to the internal stakeholders.

The payables department handles the interaction with vendors and performs transactions like the entry of invoices, vendor payments, and creation of credit and debit memos. The Receivables department tracks collections from customers.
The finance department is the owner of the Fixed Assets of the Organization. It is responsible for creating, transacting, depreciating, and retiring assets.
The financial control activities include setting up and tracking approval mechanisms, setting budgets and tracking variances, and setting up transactional controls like maker/checker and holds.
The transactions handled by the finance department are voluminous, complex, and have the potential for errors. It needs a well-designed ERP system to handle the challenges.
A well-designed ERP Accounting system should support transaction accounting and review, period-end adjustments and provisioning, period-end reconciliation, and month-end and year-end closure. The table below lists a few features that an ERP application should support.
• Real-time view of financial data
• Single source of truth: Define once, use everywhere
• Ease of reporting based on different accounting standards
• Ease of month-end and year-end processing.
• Improved cash flow and reduction in working capital requirements
• Alerts and notifications enable timely action.

| Accounting ERP Features | Feature needed by company size | Must have features |
| Supports the accounting standards of Country of Operation | All | Yes |
| Supports multiple accounting standards | Large | No |
| Allocations | All | Yes |
| Automatic reversals | All | Yes |
| Journal Approvals | All | No |
| Manual and Adjustment journals | All | Yes |
| Month-End Closure | All | Yes |
| Year-End Closure | All | Yes |
| Third party transactions (Vendor / customer) | All | Yes |
| Asset Tracking and Automatic Depreciation | All | No |
| Bank Transactions and Reconciliation | All | Yes |
| Generating Financial Reports | All | Yes |
| Ability to integrate with external applications | All | No |
| Multiple currency transactions | All | No |
| Currency revaluation and translation | Large | No |
| Excel upload and download | All | No |
| Transaction Drilldown | All | Yes |
| Create and Track Budgets | All | No |
| Country Localization | All | Yes |

An ERP for Finance should have the following applications.
This is the accounting book. Finance managers can create manual journals and period-end adjustment journals directly in the application. In addition, through internal integration, applications like payables, receivables, and assets (called sub-ledgers) transfer the accounting reflections of transactions to the General Ledger. The application uses the information collected by it to generate financial reports like Trial Balance, Balance Sheet, Profit and Loss, and Cash Flow Statement. The application is also used to create budgets and track variances.
Another name for this application is Vendor Ledger. This tracks the transactions entered with the Vendors including Invoices, Payments, Credit Memos, and Debit Memos. This application also interfaces with cash management to handle vendor payments. In the case of a full ERP setting, this application also ‘talks to’ Purchasing and Inventory applications for invoice matching purposes.
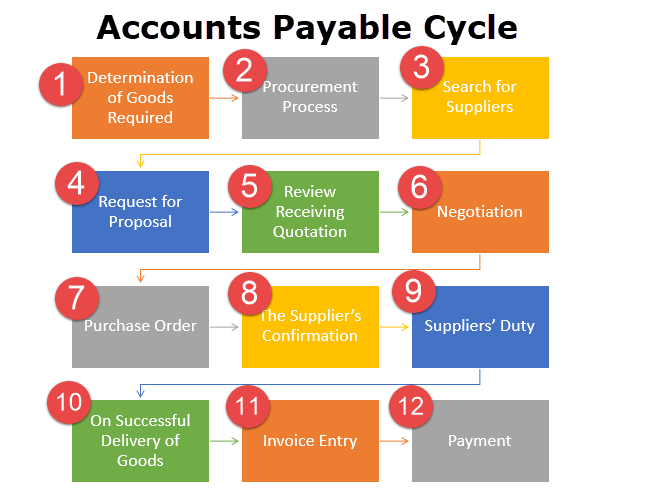
This application is also known as Customer Ledger. This application tracks Customer Invoices, Collections/receipts, and commissions for Sales Person. This application also interfaces with cash management to handle customer receipts. In a full ERP setting, this application also talks to the Shipping application for shipment information (for revenue recognition) and the Inventory application for COGS information.
This application handles cash transactions including payments and receipts. This also handles reconciliation between the bank statements and cash book.
This application owns the fixed assets of the organization and is responsible for asset creation, depreciation, and retirements. The application shares the accounting reflections of these transactions with General Ledger. This is a standalone application and is optional
This application manages the treasury operations of an organization including loans, advances, and investments. This is an optional application.

Availability of local support: This is a nice-to-have feature. With the advancement in technology and remote working, onsite/near-site support is not a mandatory requirement. Such rigid requirements may prevent you from effectively expanding to other locations.
Is the team IT Savvy? A team of young and IT-savvy people will more readily embrace technology. Their technology learning curve will be shorter.
Does the team feel the need for an ERP? If the team does not feel the need for ERP, the adoption may be slow. It is important to communicate the need for ERP to the team and ensure their buy-in.
Security and access control: ERP Applications should support role-based access to the users. For example, an invoice entry user should not have access to making payments.
Reporting flexibility: The application should have both parameterizable standard reports and flexibility to develop custom reports in the required formats
Holds: These are transaction controls used to handle uncertainties. For example, when a vendor disputes a debit note, that transaction is put on hold and remains there until the dispute is resolved. The ERP System should support holds.
 ERP Accounting FAQs
ERP Accounting FAQsAccounting systems focus on controlling financial activities whereas ERP has many functionalities including finance, sales, purchase, AR, AP, HR, Admin, and many more that centralize the business process and make decision-making faster for any company.
ERP software helps to automate the accounting process. ERP accounting system simplifies accounts payable operations, accounts receivable and improves cash flow problems with cash management. It becomes easier to manage the entire business process by generating and compiling company data.
ERP financial accounting is used for financial management. ERP Accounting Systems provides functions including profitability analysis and revenue management. ERP Accounting software is made to integrate business processes into a single software that runs on a central database.
Some of the popular examples of ERP accounting include Oracle, Ximple Solution, and SAP. Ximple Solution is specially designed for wholesale distribution accounting.
Yes, accountants used the ERP system, Accounting ERP helps them by integrating data and streamlining all of their accounting processes. ERP also helps to speed up all accounting and financial management processes that save time and money with the ability to make faster and better decisions for your business.
ERP and accounting software work separately, but ERP software provides valuable financial insights for businesses. Below are the main benefits of the ERP system for accounting for organizations.